The Effects of several natural protoberberine alkaloids and cinnamic acid derivatives used for traditional medicine on the membrane boundary potential and lipid packing stress
We are pleased to announce that Prof. Dr. Pham Quoc Long and colleagues recently published their work titled “The Effects of several natural protoberberine alkaloids and cinnamic acid derivatives used for traditional medicine on the membrane boundary potential and lipid packing stress” in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
Abstract:
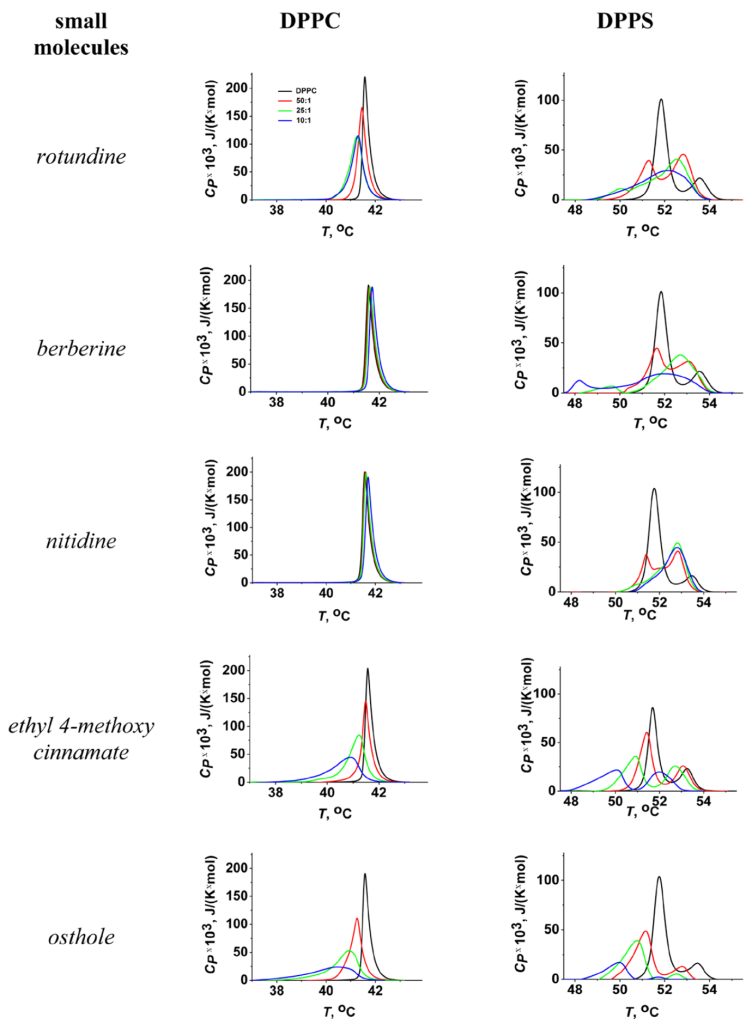
Here we elucidated the effects of natural protoberberine alkaloids (rotundine, berberine, and nitidine) and cinnamic acid derivatives (ethyl-4-methoxycinnamate and osthole) found in Vietnamese medicinal plants, on the boundary potential of lipid bilayers and phase behavior of membrane lipids. Lipid bilayers were composed of neutral phosphatidylcholines (PC) and negatively charged phosphatidylserines (PS). Tested compounds did not produce any noticeable changes in the boundary potential with the exception of osthole, which caused a potential drop by about 30 mV independently of the membrane phospholipid composition. Protoberberine alkaloids did not demonstrate an ability to greatly influence phase transition of PC, while they dramatically disturbed PS melting by integrating two different lipid states by merging the low-melting component into the higher one. Ethyl-4-methoxycinnamate and osthole were able to decrease the temperature and sharpness of the PC and PS phase transition, although the effect on PS was higher. We also revealed that ethyl-4-methoxycinnamate and osthole diminished the melting point of both components of PS transition without the changes in their relative impacts. The observed membrane activity of the tested compounds may be related to their physiological and pharmacological potential.
- Log in to post comments
